The medical experts revealed that the condition, known as BAP1 tumor predisposition syndrome, is caused by mutations in the BAP1 gene, which normally acts as a tumor suppressor, among other functions. The findings are published in JAMA Dermatology and will be presented today at the Society for Investigative Dermatology Annual Meeting in Dallas.
Scientists happened upon the discovery while studying participants who were enrolled in a screening for BAP 1 variants at the NIH Clinical Center. As part of the study, a dermatology screening was performed at enrollment and annually for participants aged 2 and older. The cohort in the current study included 47 individuals with BAP1 tumor predisposition syndrome from 35 families.
co-lead author and genetic counselor Alexandra Lebensohn, M.S., of NIH’s National Cancer Institute (NCI) said, “When asked about nail health during a baseline genetic assessment, a very astute patient reported that he had noticed subtle changes in his nails. His comment prompted us to systematically evaluate other participants for nail changes and uncover this new finding.”
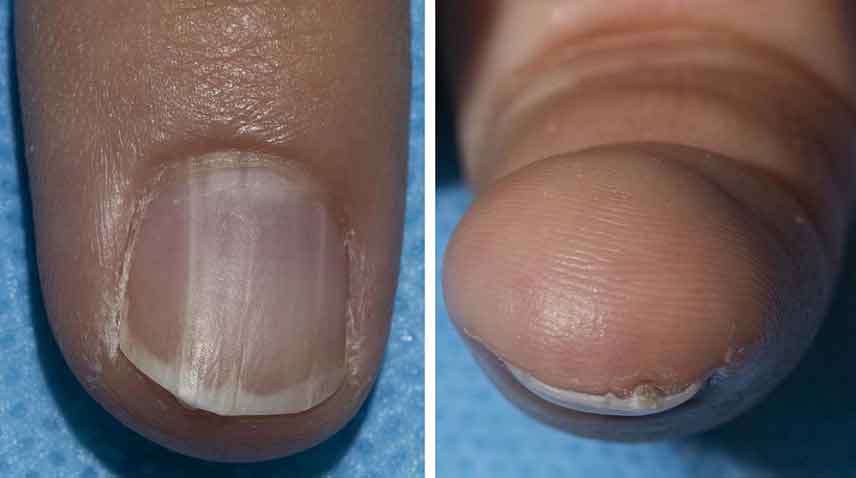
Biopsies of the nail and underlying nail bed in several participants confirmed the investigators’ suspicion of a benign tumor abnormality known as an onychopapilloma. The condition causes a colored band (usually white or red) along the length of the nail, along with thickening of the nail underlying the color change and thickening at the end of the nail. It typically only affects one nail.
However, among study participants with known BAP1 tumor predisposition syndrome aged 30 and older, 88% had onychopapilloma tumors affect multiple nails. Researchers suggest that nail screening may be particularly valuable in a patient with a personal or family history of melanoma or other potential BAP1-associated malignancy.
Edward Cowen, M.D, head of Dermatology Consultation Services at NIH’s National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases (NIAMS), said, “This finding is rarely seen in the general population, and we believe the presence of nail changes that suggest onychopapillomas on multiple nails should prompt consideration of a diagnosis of BAP1 tumor predisposition syndrome.”
“This discovery is an excellent example of how multidisciplinary teams and natural history studies can reveal insights about rare diseases,” said Raffit Hassan, M.D., co-senior author of the study and the Principal Investigator of the clinical protocol in which these patients were enrolled.
The findings were supported by the intramural programs of NIAMS (ZIAAR041229) and NCI (ZIABC010816) and included collaborations with physicians at Walter Reed National Medical Center and the Joint Pathology Center.




